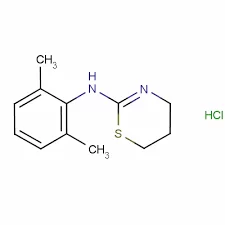
Xylazine HCl, with the molecular formula C12H16ClN3S, is a sedative and analgesic compound that acts by stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the central nervous system. This action results in sedation, analgesia, and muscle relaxation.
1. Molecular Formula: C12H16ClN3S
2. CAS Number: 23076-35-9
3. Appearance: White crystalline powder
4. Purity: 99% (suitable for research and pharmacological studies)
5. Solubility: Soluble in water, ethanol, and methanol
Xylazine HCl is a water-soluble compound that can be used in a variety of experimental settings to study its neuropharmacological effects and its impact on the nervous system.
Xylazine HCl is primarily used in veterinary medicine and research, with a range of applications:
1. Veterinary Sedative and Analgesic: Xylazine is commonly used in veterinary clinics to induce sedation, muscle relaxation, and pain relief during minor surgical procedures, diagnostic imaging, and other medical interventions in animals.
2. Research Chemical: Xylazine is valuable in neuroscience and pharmacological research to explore the mechanisms of sedation, analgesia, and muscle relaxation. Researchers use Xylazine to study the role of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the central nervous system and the sympatholytic effects of the compound.
3. Preanesthetic Agent: Xylazine is used as a preanesthetic agent to prepare animals for general anesthesia. It helps reduce the amount of anesthetic drugs required, making procedures safer and more effective.
4. Chemical Studies and Drug Development: Xylazine is an important tool in the development of new analgesic and sedative drugs. Its properties as an alpha-2 agonist make it an ideal candidate for developing novel therapeutics for pain and anxiety management.
Xylazine exerts its effects primarily by acting on alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the central nervous system. These receptors, when activated, inhibit the release of norepinephrine and other neurotransmitters, leading to:
1. Sedation: By inhibiting sympathetic nervous activity, Xylazine induces a sedative effect, calming the subject.
2. Analgesia: Xylazine produces pain relief by blocking the transmission of pain signals in the central nervous system.
3. Muscle Relaxation: It also acts as a muscle relaxant, helping to reduce muscle tone and improve comfort during surgical procedures.

Glutathione, often referred to as the body’s “master antioxidant,” has moved from relative obscurity in medical textbooks to the center of global discussion in health, wellness, and biotechnology. Once known primarily to researchers and clinicians, this naturally occurring molecule is now widely discussed in contexts ranging from chronic disease research to skincare trends and dietary supplements. As interest continues to grow, scientists, regulators, and consumers alike are reexamining what glutathione is, what it can do, and how it should be used responsibly.
With the deepening implementation of the "Made in China 2025" strategy and the rapid advancement of high-end equipment manufacturing, China's coupling industry is accelerating its transformation toward intelligent and precision-oriented development.

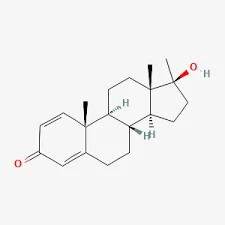
The global conversation around performance-enhancing drugs has intensified once again as anabolic steroids, particularly products marketed as Oil Dianabol, continue to surface in illegal markets. Dianabol, scientifically known as methandrostenolone, is one of the most well-known anabolic steroids in bodybuilding history. Originally developed in the mid-20th century for medical use, it has long since become controversial due to widespread misuse, health risks, and regulatory crackdowns.