4-Hydroxybenzophenone (CAS 1137-42-4) is a highly effective UV absorber used in a wide range of products to protect against harmful UV radiation. It provides exceptional stability and durability in polymer and coating applications.

Xylazine (CAS: 7361-61-7) is a potent sedative, analgesic, and muscle relaxant widely used in veterinary medicine. As a selective alpha-2 adrenergic agonist, it provides effective sedation and pain relief for a variety of animal procedures. Xylazine is also a valuable research compound for studying the mechanisms of sedation, analgesia, and autonomic nervous system regulation. Its reliability and potency make it a key tool for both clinical veterinary applications and scientific research.

Xylazine HCl (CAS: 23076-35-9) is a potent sedative, analgesic, and muscle relaxant compound commonly used in veterinary medicine. As a selective alpha-2 adrenergic agonist, it is used to induce sedation and pain relief in animals. In addition to its veterinary applications, Xylazine is also widely used in research to study the mechanisms of sedation, analgesia, and autonomic control. Its ability to provide effective sedation and muscle relaxation makes it a valuable tool in both pharmacological and neuroscience studies.

Phenacetin (CAS: 62-44-2) is a well-known analgesic and antipyretic compound historically used for pain relief and fever reduction. It serves as an important research chemical and pharmaceutical intermediate. Phenacetin is valued for its chemical stability, ease of handling, and role in the synthesis of other medicinal compounds, making it a versatile choice for medicinal chemistry studies.

Tryptamine (CAS: 61-54-1) is a naturally occurring indolealkylamine and a crucial biogenic amine found in plants, fungi, and animals. It serves as a precursor for important neurotransmitters such as serotonin and melatonin, and is widely used in research chemistry and pharmacology. Tryptamine’s unique structure allows it to participate in diverse chemical reactions, making it a versatile building block for the synthesis of bioactive compounds, including psychoactive derivatives and medicinal agents.

(2-Bromoethyl)benzene (CAS: 103-63-9) is an important organic compound commonly used in chemical synthesis, pharmaceutical research, and the production of pharmaceutical intermediates. It features a bromoethyl group attached to a benzene ring, making it an essential building block for the synthesis of a variety of bioactive molecules and pharmaceutical agents. This compound is widely utilized in medicinal chemistry and drug discovery for the development of new compounds with therapeutic potential.
Clouds

Glutathione, often referred to as the body’s “master antioxidant,” has moved from relative obscurity in medical textbooks to the center of global discussion in health, wellness, and biotechnology. Once known primarily to researchers and clinicians, this naturally occurring molecule is now widely discussed in contexts ranging from chronic disease research to skincare trends and dietary supplements. As interest continues to grow, scientists, regulators, and consumers alike are reexamining what glutathione is, what it can do, and how it should be used responsibly.
With the deepening implementation of the "Made in China 2025" strategy and the rapid advancement of high-end equipment manufacturing, China's coupling industry is accelerating its transformation toward intelligent and precision-oriented development.

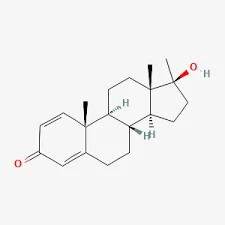
The global conversation around performance-enhancing drugs has intensified once again as anabolic steroids, particularly products marketed as Oil Dianabol, continue to surface in illegal markets. Dianabol, scientifically known as methandrostenolone, is one of the most well-known anabolic steroids in bodybuilding history. Originally developed in the mid-20th century for medical use, it has long since become controversial due to widespread misuse, health risks, and regulatory crackdowns.